Siddha Medicine is one of the indigenous medical systems that mentions around 4,448 diseases affecting humans. The human body’s functional units are Vatha, Pitta, and Kapha (Three Humors). In daily life, women face many challenges, mostly revolving around menstruation.
Menstrual disorders are a significant problem for women in India. The menstrual cycle is a series of cyclic events that occur recurrently during a woman’s reproductive lifespan. Menorrhagia, excessive menstrual bleeding, is a crucial health concern. Approximately 53 out of every 1,000 women are affected by menorrhagia. Bleeding that lasts longer than 7 days. A typical period lasts 2-7 days. Soaking through pads every hour. This may require you to change them frequently throughout the day and night.
Passing blood clots larger than a quarter. These clots can sometimes be accompanied by cramping.
Almost every woman experiences abnormal uterine bleeding at least once in her lifetime, which can interfere with her mental, physical, and overall quality of life. Menorrhagia often leads to anemia in women.
The Siddha system elaborates on women’s related diseases in the textbook “Magalir Maruthuvam.” The term “menorrhagia” is replaced with “Perumpadu” in the Siddha system.
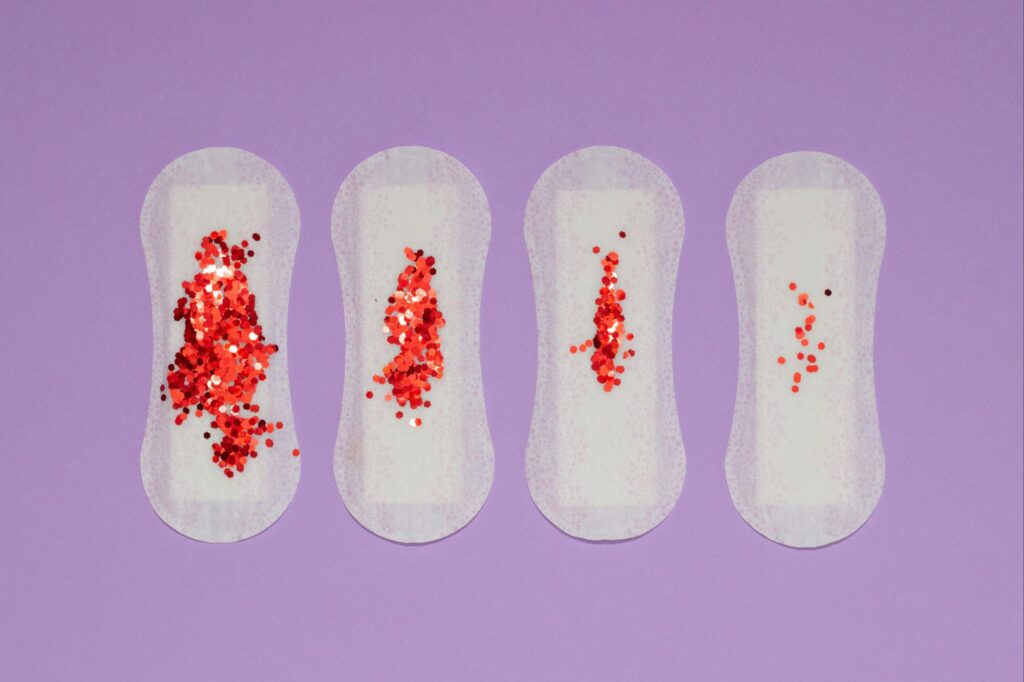
Perumpadu Rogam(menorrhagia) is a condition defined by excessive vaginal bleeding with a prolonged duration. Many Siddha texts discuss its causes, classifications, signs, and symptoms.
Types of Perumpadu
1. Abarimidha Perumpadu: Defined by excessive menstrual bleeding with regular or irregular intervals and a normal cycle duration.
2. Adhama Perumpadu: Defined as intracyclic bleeding.
Causes of Perumpadu
- Exposure to heat,
- Excessive intercourse,
- Irritation of the external genitalia,
- Excessive anger,
- Tumors in the uterus,
- Abortions
- Sexual intercourse during their menstrual period,
- Hormonal imbalances,
- Dysfunctional ovaries,
- Uterine fibroids,
- Polyps,
- Adenomyosis,
- Intrauterine devices (IUDs), Pregnancy complications,
- Cancer, Inherited bleeding disorders, or take certain medications .
Premonitory Signs and Symptoms
- Heavy vaginal bleeding, resulting in the saturation of one or more sanitary pads every hour for several hours.
- Lower back pain
- lower abdominal pain,
- headache.
Common Signs and Symptoms

- Excessive menstrual flow with an unpleasant odor,
- reddish-black in color with blood clots, and palpitation.
- Abdominal distention,
- vaginal inflammation,
- pallor of the body, and boring pain in the limbs.
Etiology in Siddha Aspect
There are two major types of perumpadu (menorrhagia):
1. Sadharana Perumpadu
2. Asadharana Perumpadu
Sadharana Perumpadu
- Fibroid uterus or uterine polyps
- Pelvic tumors
- Genital tuberculosis (starting stage)
- Endocrine disorders
- Psychiatric illness
Asadharana Perumpadu
Based on symptoms and age, it can be classified as:
- Excessive bleeding in adolescence
- Postpartum bleeding
- Postmenopausal bleeding in old age.
Classification According to Siddha Literature
Yugimuni classified perumpadu into four types:
1. Vatha Perumpadu
2. Pitha Perumpadu
3. Kabha Perumpadu
4. Thondha Perumpadu
All four types of Perumpadu Rogam involve vaginal bleeding with different colors.
Symptoms of Vatha Perumpadu:
- Pelvic and abdominal pain
- Headache
- Low back pain
- Body complexion changes to black
- Pain in the lower abdomen
- Menstrual bleeding is reddish-black in color
Symptoms of Pitha Perumpadu:
- Burning sensation of the body and burning pain in the vagina
Symptoms of Kapa Perumpadu:
- Foul smell
- Pale body
- Dyspnea on exertion
- Fainting
Symptoms of Thondha Perumpadu:
- Excessive salivation
- Foul smell
- Pelvic and abdominal pain
- Abdominal discomfort
- Backache
Menstruation-physiology of Siddha:
Vata humor is responsible for the maturation and movement of the follicle, its rupture, and the release of the ovum during the ovarian cycle. Pitta dosha, the energy of transformation, expresses the nature of hormones and assists in the rupture of the follicle. Kapha dosha, with its heavy and cool qualities, nourishes the tissues of the uterus (endometrium) and the entire reproductive system.
Modern Medical Investigations
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Peripheral blood smear
Bleeding time, clotting time
Thyroid function tests
Ultrasonography and color doppler study of pelvis
Treatment
Vata humor (Vali) becomes imbalanced, which can also affect Pitta dosha (Azhal) and Kapha dosha (Iyham) consequently.
The first step is to bring the three humors (doshas) back into equilibrium. To address the imbalanced Vata dosha (Vali) initially, we recommend bowel cleansing methods. There are various medicines available. Proper dietary guidelines (Pathya) are essential to optimize the results of the medication. However, a medicine that cures one person may not cure another, depending on the specific condition.
Internal Medicines:
1. Aththi kudineer (60-100 ml, BD, after food)
2. Asoka Pattai kudineer (60-100 ml, BD, after food)
3. Othiyampattai kudineer (1-2 gm with buttermilk, BD, after food)
4. Kavikkal choornam
5. Vazhai poo vadagam (500mg) – 1-2 chewable tablets, BD/TDS, after food
6. Impooral vadagam (500mg) – 1-2 chewable tablets, BD/TDS, after food
7. Impooral Ilagam: 5-10 gm with warm milk, BD, after food
Home Remedies
Asoku (Saraca asoka) bark boiled with cow’s milk and bark dried in sunshade and its powder combine with milk given for menorrhagia during the 4th day of the menstrual cycle.
Heavy menstrual bleeding powder of the bark of Naaval mixed with butter milk or curd’
Grind the thumba leaf and take a lemon-sized portion. Mix it with 30 ml of sesame oil and consume only in the morning for 7 days to cure the disease.
Crush 10 grams of navalpattai and add 200 ml of water. Boil it until it reduces to 50 ml. Filter and give it twice a day.
Extract the juice of a whole banana flower and add a spoon of curd. Consume it on an empty stomach in the morning for three days to cure menstrual cramps and bleeding.
Thottasinungi Kudineer for Menorrhagia: Take 50 g of Thottarsurungi whole plant (Mimosa pudica), crush it and boil with 200 ml of water. Reduce the quantity. From that take 30 – 60 ml of decoction depends upon the disease condition.

Medical Advice:
Cool, less salty food with astringent properties is recommended. Include more banana flowers in your diet and prioritize rest. Avoid sugary and high-sodium foods. Some beneficial options include:
Sakkaravalli kizhangu (Ipomoea batatas)
Seppankizhangu (Colocasia esculenta)
Kothavarai (Cyamopsis tetragonoloba)
Kollu (Macrotyloma uniflorum)
Take a hot water hip bath routinely for 10 minutes at a temperature of 50°C to 60°C.
Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, range-of-motion exercises to keep joints mobile, relaxed walking promote good oxygenation and circulation and can even help increase energy.
Avoid oral contraceptives and caffeine-containing beverages.
Conclusion:
Siddha is a unique system that treats both the disease and the overall state of the patient as well. By raising awareness about the traditional system of Magalir Maruthuvam and its treatments for women’s health issues, we can improve their quality of life.
Disclaimer: Siddha treatment is based on complete physical examination of the patient, Naadi diagnosis, and other diagnostic criteria of the disease. The content given in this article is purely meant for information and education purpose only. Kindly consult a Siddha physician before any sort of self medication.

Dr. Augastina B.S.M.S., PGDY, is a passionate Siddha Doctor with a heart of gold. She believes in healing one step at a time. In her writing, you’ll find not just knowledge, but genuine care and a holistic approach to health and well-being.